After four decades of progress in Quantum Key Distribution (QKD), the demand for unconditional security in real-world networks has never been more critical. As part of the Allegro project, we’ve explored an advanced Measurement Device Independent (MDI) QKD protocol that reshapes how we approach secure quantum communications.
✨ Why MDI-QKD Matters
Introduced by Lo et al. [2012], MDI-QKD was revolutionary because:
- It moves the measurement unit (MU) to an untrusted third party, making the system immune to detector-based side-channel attacks.
- It extends communication distances, laying the foundation for modern protocols like Twin-Field and Mode-Pairing QKD.
📡 Our Contribution: Multi-User MDI-QKD Protocol
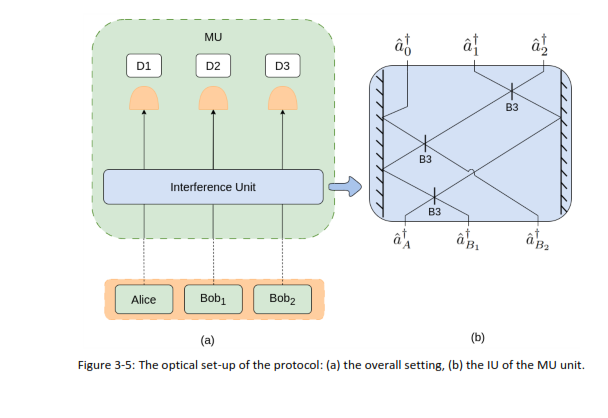
Developed by researchers at EUL [Ste25], this enhanced protocol enables pairwise key distribution among three users—using just one measurement unit, instead of three. Users independently encode their bits using phase-encoded coherent states and send them to a central MU composed of three beam splitters and photon detectors.
✅ Key Advantages:
- Efficient architecture: Single MU handles three users.
- Minimal discards: Basis matching between all users isn’t required.
- Robust to untrusted infrastructure: Maintains security even if the MU is compromised.
⚠️ Trade-offs to Consider:
- Requires synchronized signal arrival from all users.
- Slightly reduced maximum distance compared to standard MDI setups.
- Introduces a systematic error that impacts the Secure Key Rate (SKR).
💡 Still, this protocol represents a major step toward scalable and secure quantum communication networks—where security is proven by physics, not assumptions.
#QuantumTech #QKD #MDIQKD #AllegroProject #QuantumSecurity #Photonics #QuantumInternet #Cybersecurity #SecureCommunication #LinkedInScience